Power presses are industrial machines used for shaping or cutting metal and other materials using high-pressure mechanical force. They are widely used in manufacturing industries for operations like stamping, punching, bending, and forming. Power presses come in different types, each designed for specific tasks and applications. In this article, we will explore the various components of different types of power presses, including C-type, H-type, pneumatic, and cross-shaft power presses, their working principles, benefits, sturdiness, and global supply.
C-Type Power Press
Components of C-Type Power Press
- Frame: The C-shaped frame, made of high-quality steel, provides structural support and absorbs the energy generated during the pressing process. The C-type frame is designed for easy tool changing and better access.
- Ram: The ram is the movable part of the power press, which carries the tool and applies the necessary force to the workpiece.
- Crank Mechanism: In C-type presses, a crank mechanism is used to convert rotational motion into linear motion for the ram. This mechanism ensures consistent and reliable operation.
- Clutch and Brake Mechanism: The clutch connects or disconnects the flywheel to the drive mechanism, while the brake stops the ram when required.
- Flywheel: The flywheel stores energy and helps in maintaining continuous movement during operation.
- Lubrication System: Essential for reducing friction and ensuring smooth operation, the lubrication system helps keep the parts well-oiled.
Working Principle of C-Type Power Press
The working principle of a C-type power press involves converting rotary motion from the motor into linear motion using the crank mechanism. The flywheel stores energy, and when the clutch is engaged, the energy is transferred to the ram, which applies force on the workpiece. The ram moves in a straight line, making it ideal for operations like blanking, punching, and stamping.
What Our Customers Say
“Nice company to be deal with,have best experience for sales n after sales services, good staff too.”
Jignesh Thakkar On Google
Applications
- Metal stamping
- Die-cutting
- Coining
- Sheet metal operations
Benefits and Sturdiness
- Benefits: C-type power presses offer easy accessibility to the tooling area, making them user-friendly. They are efficient for lighter to moderate work and are known for their durability.
- Sturdiness: The C-shaped frame is highly sturdy and can withstand significant pressure. This design offers balance and prevents misalignment during heavy-duty applications.
H-Type Power Press
Components of H-Type Power Press
- H-Frame: The H-type press features an H-shaped frame, which is stronger and more rigid than the C-type. The design provides better load distribution and enhanced stability during operation.
- Slide: The slide or ram moves up and down to exert force on the material.
- Motor and Gearbox: The motor provides power to the gearbox, which converts rotational energy to linear motion, driving the ram.
- Clutch-Brake System: A dual clutch-brake system allows for smooth and safe operation by engaging or disengaging the motion of the ram.
- Lubrication System: Like other power presses, the lubrication system minimizes wear and tear on the components.
Working Principle of H-Type Power Press
The H-type power press operates on the same principle as the C-type, but with a more rigid frame. The motor drives a gearbox, which converts rotational motion to linear motion of the ram. The heavy-duty frame ensures stability, even under high force conditions. This design is often used for heavy-duty operations, where larger workpieces and high pressures are involved.
Applications
- Heavy metal stamping
- Automotive part manufacturing
- Deep drawing and bending
- Cutting and punching of large workpieces
Benefits and Sturdiness
- Benefits: H-type presses are known for their superior rigidity and ability to handle high tonnages. They are suitable for large-scale production runs and can operate under heavy loads.
- Sturdiness: The H-shaped frame provides maximum rigidity and stability, allowing the press to handle heavier loads without excessive wear and tear.
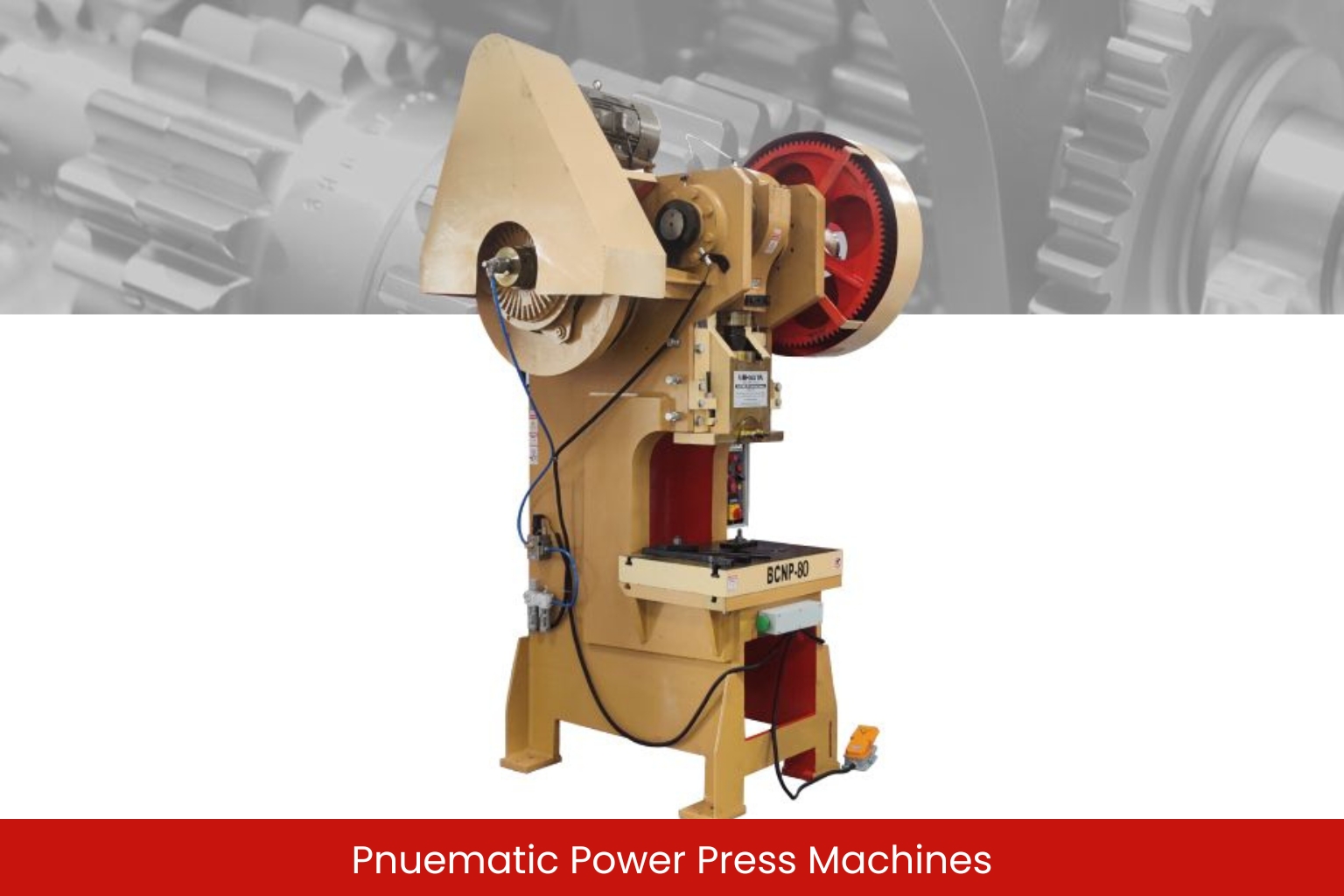
Pneumatic Power Press
Components of Pneumatic Power Press
- Pneumatic Cylinder: This component uses compressed air to generate force, which drives the ram.
- Frame: The frame is generally made of high-strength steel or cast iron, designed to handle the pressure generated by the pneumatic force.
- Ram: The ram is the moving part that directly applies force to the material.
- Air Compressor: An air compressor generates the necessary air pressure required to operate the pneumatic system.
- Control Valve: A valve system controls the airflow, regulating the speed and force of the ram.
Working Principle of Pneumatic Power Press
A pneumatic power press uses compressed air to drive the ram. When air is released into the pneumatic cylinder, it pushes the ram downwards with considerable force. The force applied depends on the air pressure, which can be adjusted for different operations. This type of press is commonly used for light to medium operations like punching, riveting, and assembly.
Applications
- Light metal stamping
- Riveting
- Assembling small parts
- Plastic forming
Benefits and Sturdiness
- Benefits: Pneumatic presses are quieter and cleaner compared to mechanical presses, making them suitable for applications in environments where noise reduction is a priority. They are also more energy-efficient for certain operations.
- Sturdiness: While pneumatic presses are not as robust as mechanical presses, their simpler design makes them reliable and easy to maintain, especially for low to medium force applications.
Cross Shaft Power Press
Components of Cross Shaft Power Press
- Cross Shaft Mechanism: The most distinct feature of this power press is the cross shaft, which transmits rotary motion across the machine’s width. This mechanism allows for more precise control of the ram.
- Frame: Similar to other presses, the frame is made from high-strength steel to bear the load and vibrations during operation.
- Clutch and Brake: A clutch and brake system is used to control the operation of the ram, providing both speed and safety during operation.
- Flywheel: The flywheel stores rotational energy and assists with maintaining a steady speed for the ram.
- Lubrication System: Keeps all moving parts well-oiled to reduce friction and wear.
Working Principle of Cross Shaft Power Press
The cross-shaft power press uses a set of shafts positioned across the width of the press to drive the ram with greater precision. The rotational motion of the flywheel is transferred through the shaft system, which then moves the ram. This allows for more uniform and controlled movement, ideal for intricate operations.
Applications
- Precision metalworking
- Coining and embossing
- Fine stamping
- Thin metal sheet processing
Benefits and Sturdiness
- Benefits: The cross shaft press is known for its precision and ability to handle intricate, detailed work. The ability to distribute force evenly across the machine results in consistent quality in the finished product.
- Sturdiness: The cross shaft mechanism is highly stable, ensuring precise movements even in high-precision applications.
Global Supply and Market
The global supply of power presses is driven by the growing demand for automated manufacturing processes, particularly in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Countries like China, Germany, the United States, and Japan are leading suppliers of various types of power presses. The market is expected to grow due to the increasing adoption of robotics and automation in manufacturing.
Challenges in Global Supply
- Cost: High-quality power presses can be expensive, which may limit their availability in certain regions.
- Maintenance and Service: Regular maintenance is required to keep power presses in optimal condition, which can be a challenge in remote areas.
- Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological change is leading to the development of more efficient and advanced power presses, with features like CNC controls, increased automation, and higher energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Power presses are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, offering a wide range of benefits depending on the type and application. C-type, H-type, pneumatic, and cross-shaft power presses each have unique components and working principles that make them suitable for specific tasks. While their sturdiness and benefits vary, all types of power presses contribute to increased efficiency and precision in production processes. The global supply of these machines is expanding, driven by technological advancements and the need for high-volume manufacturing solutions.
FAQs: Power Press
What is the main difference between C-type and H-type power presses?
- C-Type Power Press: Features a C-shaped frame, suitable for lighter to moderate work. It provides easy access to tooling but is less rigid than the H-type.
- H-Type Power Press: Has an H-shaped frame that offers superior rigidity and stability, making it ideal for heavy-duty operations, such as large-scale stamping and deep drawing.
How does a pneumatic power press work?
A pneumatic power press uses compressed air to drive a cylinder, which moves the ram. The amount of air pressure determines the force applied to the workpiece. Pneumatic presses are typically used for lighter operations like riveting and assembling.
What are the primary applications of a cross-shaft power press?
Cross-shaft power presses are ideal for applications requiring high precision, such as fine stamping, coining, and embossing. They are used in industries that require detailed and uniform metalworking, including the coinage industry and for processing thin metal sheets.
What are the benefits of using a C-type power press over an H-type?
- C-Type Power Press: Easier tool changeover and accessibility. It is ideal for lighter workloads, making it more cost-effective and suitable for smaller production runs or detailed work.
- H-Type Power Press: More rigid and capable of handling larger workpieces under higher tonnage. It is ideal for heavy-duty operations.
Which power press is better for heavy-duty industrial applications?
The H-type power press is better suited for heavy-duty applications due to its robust H-shaped frame, which provides more stability and load-bearing capacity compared to the C-type press.
Can pneumatic power presses be used for heavy operations?
No, pneumatic power presses are generally used for lighter operations. They are not suited for high-tonnage tasks or heavy stamping, as the force they can generate is limited by air pressure. For heavy-duty operations, mechanical presses like C-type and H-type are recommended.
What are the key advantages of using a pneumatic power press over mechanical presses?
Pneumatic power presses are quieter, cleaner, and require less maintenance compared to mechanical presses. They are energy-efficient and suitable for light-to-medium-duty operations where the speed and precision of the ram are more important than high force.
How does the clutch-brake system in power presses work?
The clutch is used to engage or disengage the motion of the ram, while the brake stops the ram after each stroke. This system ensures precise control over the press's operation, preventing accidents and providing safety features by halting the ram when needed.
Are cross-shaft power presses more precise than other types?
Yes, cross-shaft power presses offer higher precision due to their mechanism, which distributes force evenly and ensures more controlled movements. This makes them ideal for operations that require fine detail and consistency.
What is the role of the flywheel in a power press?
The flywheel stores rotational energy and helps maintain a steady speed during the operation of the press. It ensures that the ram moves continuously, even during the transition between strokes, providing consistent force on the material.
What factors should be considered when choosing a power press?
- Type of Operation: Consider the nature of the work (e.g., light vs. heavy-duty).
- Precision: For high-precision tasks, cross-shaft or H-type presses are ideal.
- Tonnage: Choose based on the force needed for the material.
- Space and Accessibility: C-type presses are easier to access, while H-type presses are bulkier but offer more rigidity.
- Maintenance Needs: Pneumatic presses require less maintenance, but mechanical presses might last longer under heavy use.
Are power presses easy to maintain?
Maintenance depends on the type of press. Pneumatic presses require less frequent maintenance but may have limited life cycles under heavy use. Mechanical presses, especially C-type and H-type, require regular lubrication, clutch-brake checks, and alignment adjustments, but they are built to last longer.
What are the global suppliers of power presses?
Key suppliers of power presses include countries like India, Germany, Japan, China, and the United States. These countries manufacture a wide range of power presses catering to industries like automotive, aerospace, and metalworking.
Can power presses be automated?
Yes, modern power presses, especially C-type, H-type, and cross-shaft types, can be integrated with automation systems. This includes robotic arms, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and CNC controls, allowing for high-volume, precision operations with minimal manual intervention.
What safety measures are typically in place for power presses?
Power presses are equipped with safety mechanisms like:
- Two-hand safety control: Ensures operators are a safe distance from the machine.
- Clutch-brake system: Helps to prevent the ram from engaging unexpectedly.
- Guarding systems: Physical barriers or sensors to prevent injury.